一维插值#
分段线性插值#
如果只需要线性(又称折线)插值,可以使用 numpy.interp 例程。它接受两个用于插值的数据数组 x 和 y,以及第三个数组 xnew,其中包含要评估插值的点。
>>> import numpy as np
>>> x = np.linspace(0, 10, num=11)
>>> y = np.cos(-x**2 / 9.0)
构建插值
>>> xnew = np.linspace(0, 10, num=1001)
>>> ynew = np.interp(xnew, x, y)
并绘制它
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
>>> plt.plot(xnew, ynew, '-', label='linear interp')
>>> plt.plot(x, y, 'o', label='data')
>>> plt.legend(loc='best')
>>> plt.show()
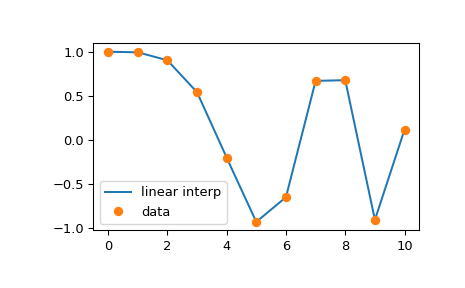
numpy.interp 的一个限制是它不允许控制外推。有关提供此类功能的替代例程,请参阅B-样条插值部分。
三次样条#
当然,分段线性插值会在数据点处产生尖角,线性段在此处连接。为了产生更平滑的曲线,可以使用三次样条,其中插值曲线由具有匹配一阶和二阶导数的三次分段组成。在代码中,这些对象通过 CubicSpline 类实例表示。实例使用数据数组 x 和 y 构造,然后可以使用目标 xnew 值进行评估
>>> from scipy.interpolate import CubicSpline
>>> spl = CubicSpline([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6], [1, 4, 8, 16, 25, 36])
>>> spl(2.5)
5.57
一个 CubicSpline 对象的 __call__ 方法接受标量值和数组。它还接受第二个参数 nu,用于评估 nu 阶导数。例如,我们绘制样条的导数
>>> from scipy.interpolate import CubicSpline
>>> x = np.linspace(0, 10, num=11)
>>> y = np.cos(-x**2 / 9.)
>>> spl = CubicSpline(x, y)
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
>>> fig, ax = plt.subplots(4, 1, figsize=(5, 7))
>>> xnew = np.linspace(0, 10, num=1001)
>>> ax[0].plot(xnew, spl(xnew))
>>> ax[0].plot(x, y, 'o', label='data')
>>> ax[1].plot(xnew, spl(xnew, nu=1), '--', label='1st derivative')
>>> ax[2].plot(xnew, spl(xnew, nu=2), '--', label='2nd derivative')
>>> ax[3].plot(xnew, spl(xnew, nu=3), '--', label='3rd derivative')
>>> for j in range(4):
... ax[j].legend(loc='best')
>>> plt.tight_layout()
>>> plt.show()
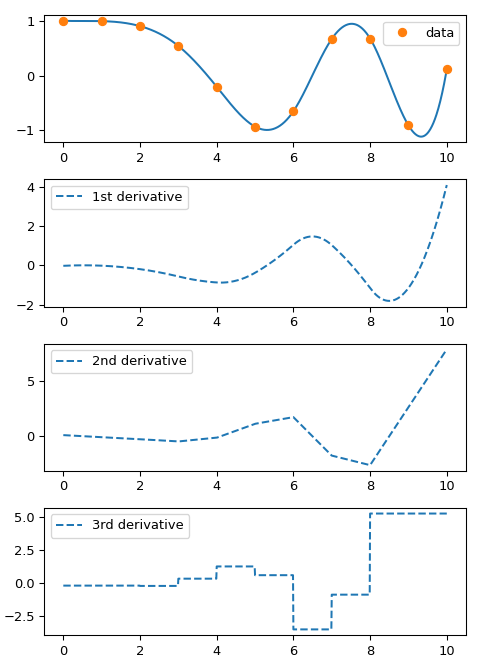
请注意,一阶和二阶导数通过构造是连续的,而三阶导数在数据点处发生跳变。
单调插值器#
三次样条通过构造是二阶连续可微的。这可能导致样条函数在数据点之间振荡和“超调”。在这些情况下,一种替代方法是使用所谓的*单调*三次插值器:这些插值器被构造为仅一阶连续可微,并试图保留数据所暗示的局部形状。scipy.interpolate 提供了两种此类对象:PchipInterpolator 和 Akima1DInterpolator。为了说明这一点,我们考虑包含离群值的数据
>>> from scipy.interpolate import CubicSpline, PchipInterpolator, Akima1DInterpolator
>>> x = np.array([1., 2., 3., 4., 4.5, 5., 6., 7., 8])
>>> y = x**2
>>> y[4] += 101
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
>>> xx = np.linspace(1, 8, 51)
>>> plt.plot(xx, CubicSpline(x, y)(xx), '--', label='spline')
>>> plt.plot(xx, Akima1DInterpolator(x, y)(xx), '-', label='Akima1D')
>>> plt.plot(xx, PchipInterpolator(x, y)(xx), '-', label='pchip')
>>> plt.plot(x, y, 'o')
>>> plt.legend()
>>> plt.show()
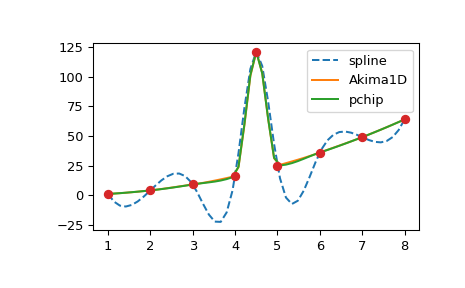
B-样条插值#
B-样条构成了分段多项式的另一种(如果形式上等效的)表示。这种基通常比幂基在计算上更稳定,并且适用于包括插值、回归和曲线表示在内的各种应用。详细信息请参阅分段多项式部分,在此我们通过构建正弦函数的插值来说明其用法
>>> x = np.linspace(0, 3/2, 7)
>>> y = np.sin(np.pi*x)
给定数据数组 x 和 y,为了构造插值对象,我们使用 make_interp_spline 函数
>>> from scipy.interpolate import make_interp_spline
>>> bspl = make_interp_spline(x, y, k=3)
此函数返回一个对象,该对象的接口类似于 CubicSpline 对象。特别是,它可以在数据点处进行评估和求导
>>> der = bspl.derivative() # a BSpline representing the derivative
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
>>> xx = np.linspace(0, 3/2, 51)
>>> plt.plot(xx, bspl(xx), '--', label=r'$\sin(\pi x)$ approx')
>>> plt.plot(x, y, 'o', label='data')
>>> plt.plot(xx, der(xx)/np.pi, '--', label=r'$d \sin(\pi x)/dx / \pi$ approx')
>>> plt.legend()
>>> plt.show()
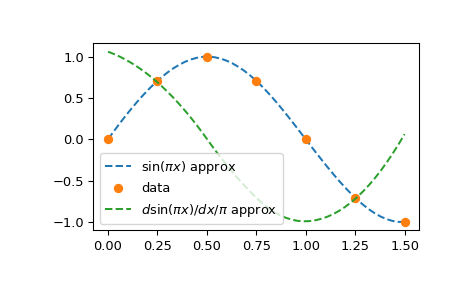
请注意,通过在调用 make_interp_spline 中指定 k=3,我们请求了一个三次样条(这是默认值,因此 k=3 可以省略);三次函数的导数是二次函数
>>> bspl.k, der.k
(3, 2)
默认情况下,make_interp_spline(x, y) 的结果等效于 CubicSpline(x, y)。区别在于前者允许多种可选功能:它可以构造不同次数的样条(通过可选参数 k)和预定义节点(通过可选参数 t)。
样条插值的边界条件可以通过 make_interp_spline 函数和 CubicSpline 构造函数的 bc_type 参数来控制。默认情况下,两者都使用“not-a-knot”边界条件。
非三次样条#
make_interp_spline 的一个用途是构造具有线性外推的线性插值器,因为 make_interp_spline 默认进行外推。请考虑
>>> from scipy.interpolate import make_interp_spline
>>> x = np.linspace(0, 5, 11)
>>> y = 2*x
>>> spl = make_interp_spline(x, y, k=1) # k=1: linear
>>> spl([-1, 6])
[-2., 12.]
>>> np.interp([-1, 6], x, y)
[0., 10.]
更多详细信息和讨论请参阅外推部分。
y 的批次#
单变量插值器不仅接受一维 y 数组,还接受 y.ndim > 1 的数组。其解释是 y 是 1D 数据数组的*批次*:默认情况下,y 的零维是插值轴,而尾随维度是批次维度。考虑在点 \(x_i\) 处采样的函数集合(一个*批次*)\(f_j\)。我们可以通过提供一个二维数组 y,使得 y[i, j] 记录 \(f_j(x_i)\),从而为所有这些函数实例化一个插值器。
举例说明
>>> import numpy as np
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
>>> from scipy.interpolate import make_interp_spline
>>> n = 11
>>> x = 2 * np.pi * np.arange(n) / n
>>> x.shape
(11,)
>>> y = np.stack((np.sin(x)**2, np.cos(x)), axis=1)
>>> y.shape
(11, 2)
>>> spl = make_interp_spline(x, y)
>>> xv = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, 51)
>>> plt.plot(x, y, 'o')
>>> plt.plot(xv, spl(xv), '-')
>>> plt.show()
需要注意几点。首先,这里的行为看起来类似于 NumPy 的广播,但在两个方面有所不同
即使
y数组不是一维的,x数组也应为一维:即x.ndim == 1而y.ndim >= 1。x与y之间没有广播。默认情况下,*尾随*维度用作批次维度,这与 NumPy 使用*前导*维度作为批次维度的约定不同。
其次,插值轴可以通过可选的 axis 参数控制。上面的例子使用了 axis=0 的默认值。对于非默认值,以下情况成立
y.shape[axis] == x.size(否则会引发错误)spl(xv)的形状是y.shape[axis:] + xv.shape + y.shape[:axis]
虽然我们使用 make_interp_spline 演示了批处理行为,但实际上大多数单变量插值器都支持此功能:PchipInterpolator 和 Akima1DInterpolator、CubicSpline;低阶多项式表示类 PPoly、BPoly 和 BSpline;以及最小二乘拟合和样条平滑函数 make_lsq_spline 和 make_smoothing_spline。
参数样条曲线#
到目前为止,我们考虑了样条*函数*,其中数据 y 预期显式依赖于自变量 x——因此插值函数满足 \(f(x_j) = y_j\)。样条*曲线*将 x 和 y 数组视为平面上点 \(\mathbf{p}_j\) 的坐标,并且通过这些点的插值曲线由某个附加参数(通常称为 u)参数化。请注意,这种构造很容易推广到更高维度,其中 \(\mathbf{p}_j\) 是 N 维空间中的点。
样条曲线可以很容易地通过插值函数处理多维数据数组的特性来构造,如上一节所述。对应于数据点的参数 u 的值需要由用户单独提供。
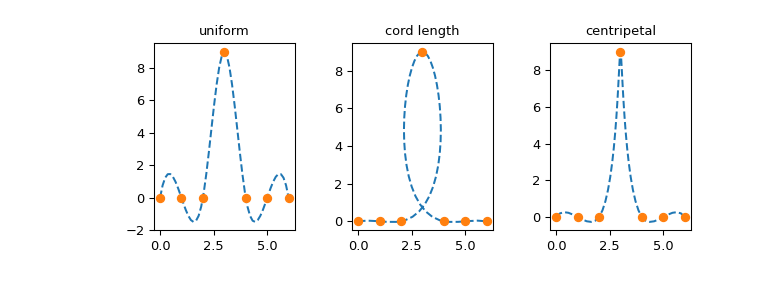
参数化的选择取决于具体问题,不同的参数化可能会产生截然不同的曲线。例如,我们考虑一个(有些困难的)数据集的三种参数化,这些数据取自 BSpline 文档字符串中列出的参考文献 [1] 的第 6 章
>>> x = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
>>> y = [0, 0, 0, 9, 0, 0, 0]
>>> p = np.stack((x, y))
>>> p
array([[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6],
[0, 0, 0, 9, 0, 0, 0]])
我们将数组 p 的元素作为平面上七个点的坐标,其中 p[:, j] 给出点 \(\mathbf{p}_j\) 的坐标。
首先,考虑*均匀*参数化,\(u_j = j\)
>>> u_unif = x
其次,我们考虑所谓的*弦长*参数化,它不过是连接数据点的直线段的累积长度
对于 \(j=1, 2, \dots\) 和 \(u_0 = 0\)。其中 \(| \cdots |\) 是平面上连续点 \(p_j\) 之间的长度。
>>> dp = p[:, 1:] - p[:, :-1] # 2-vector distances between points
>>> l = (dp**2).sum(axis=0) # squares of lengths of 2-vectors between points
>>> u_cord = np.sqrt(l).cumsum() # cumulative sums of 2-norms
>>> u_cord = np.r_[0, u_cord] # the first point is parameterized at zero
最后,我们考虑有时被称为*向心*参数化:\(u_j = u_{j-1} + |\mathbf{p}_j - \mathbf{p}_{j-1}|^{1/2}\)。由于额外的平方根,连续值 \(u_j - u_{j-1}\) 之间的差异将小于弦长参数化的情况。
>>> u_c = np.r_[0, np.cumsum((dp**2).sum(axis=0)**0.25)]
现在绘制结果曲线
>>> from scipy.interpolate import make_interp_spline
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
>>> fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 3, figsize=(8, 3))
>>> parametrizations = ['uniform', 'cord length', 'centripetal']
>>>
>>> for j, u in enumerate([u_unif, u_cord, u_c]):
... spl = make_interp_spline(u, p, axis=1) # note p is a 2D array
...
... uu = np.linspace(u[0], u[-1], 51)
... xx, yy = spl(uu)
...
... ax[j].plot(xx, yy, '--')
... ax[j].plot(p[0, :], p[1, :], 'o')
... ax[j].set_title(parametrizations[j])
>>> plt.show()
缺失数据#
我们注意到 scipy.interpolate *不*支持带缺失数据的插值。表示缺失数据的两种常用方法是使用 numpy.ma 库的掩码数组,以及将缺失值编码为非数字 NaN。
scipy.interpolate 不直接支持这两种方法。个别例程可能提供部分支持和/或变通方案,但总的来说,该库严格遵循 IEEE 754 语义,其中 NaN 表示*非数字*,即非法数学运算(例如除以零)的结果,而不是*缺失*。
一维插值的旧版接口 (interp1d)#
scipy.interpolate 中的 interp1d 类是一种方便的方法,用于根据固定数据点创建函数,该函数可以使用线性插值在给定数据定义的域内的任何位置进行评估。通过传递包含数据的 1D 向量来创建此类的实例。此类的实例定义了一个 __call__ 方法,因此可以像函数一样处理,该函数在已知数据值之间进行插值以获得未知值。边界处的行为可以在实例化时指定。以下示例演示了其在线性插值和三次样条插值中的使用
>>> from scipy.interpolate import interp1d
>>> x = np.linspace(0, 10, num=11, endpoint=True)
>>> y = np.cos(-x**2/9.0)
>>> f = interp1d(x, y)
>>> f2 = interp1d(x, y, kind='cubic')
>>> xnew = np.linspace(0, 10, num=41, endpoint=True)
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
>>> plt.plot(x, y, 'o', xnew, f(xnew), '-', xnew, f2(xnew), '--')
>>> plt.legend(['data', 'linear', 'cubic'], loc='best')
>>> plt.show()
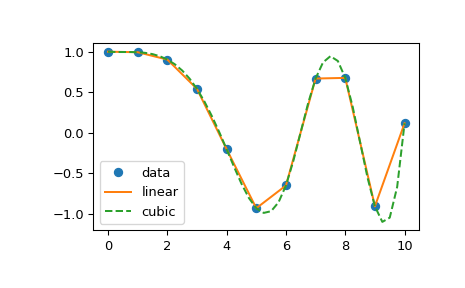
interp1d 的“cubic”类型等效于 make_interp_spline,而“linear”类型等效于 numpy.interp,同时还允许 N 维 y 数组。
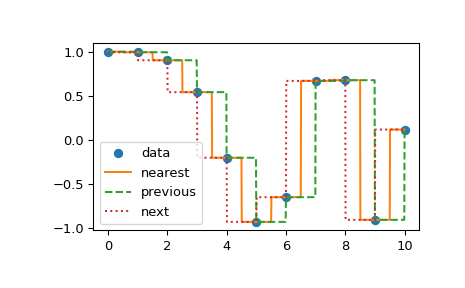
interp1d 中的另一组插值是*最近*、*前一个*和*下一个*,它们返回沿着 x 轴最近的、前一个或下一个点。最近和下一个可以被认为是因果插值滤波器的特殊情况。以下示例演示了它们的使用,使用与前一个示例相同的数据
>>> from scipy.interpolate import interp1d
>>> x = np.linspace(0, 10, num=11, endpoint=True)
>>> y = np.cos(-x**2/9.0)
>>> f1 = interp1d(x, y, kind='nearest')
>>> f2 = interp1d(x, y, kind='previous')
>>> f3 = interp1d(x, y, kind='next')
>>> xnew = np.linspace(0, 10, num=1001, endpoint=True)
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
>>> plt.plot(x, y, 'o')
>>> plt.plot(xnew, f1(xnew), '-', xnew, f2(xnew), '--', xnew, f3(xnew), ':')
>>> plt.legend(['data', 'nearest', 'previous', 'next'], loc='best')
>>> plt.show()
interp1d 模式的推荐替代品#
如前所述,interp1d 类是*旧版*的:我们没有计划将其移除;我们将继续支持其现有用法;但我们认为有更好的替代方案,建议在新代码中使用。
这里我们根据插值 kind 列出具体建议。
线性插值,kind="linear"
默认建议是使用 numpy.interp 函数。或者,您可以使用线性样条,即 make_interp_spline(x, y, k=1),请参阅本节讨论。
样条插值器,kind="quadratic" 或 "cubic"
在底层,interp1d 委托给 make_interp_spline,因此我们建议直接使用后者。
分段常数模式,kind="nearest", "previous", "next"
首先,我们注意到 interp1d(x, y, kind='previous') 等效于 make_interp_spline(x, y, k=0)。
然而,更普遍地说,所有这些分段常数插值模式都基于 numpy.searchsorted。例如,“nearest”模式只不过是
>>> x = np.arange(8)
>>> y = x**2
>>> x_new = np.linspace(0, 7, 101) # input points
>>> x_bds = x[:-1] / 2.0 + x[1:] / 2.0 # halfway points
>>> idx = np.searchsorted(x_bds, x_new, side='left')
>>> idx = np.clip(idx, 0, len(x) - 1) # clip the indices so that they are within the range of x indices.
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
>>> plt.plot(x, y, 'o')
>>> plt.plot(x_new, y[idx], '--')
>>> plt.show()
其他变体类似,详情请参阅 interp1d 源代码。