scipy.interpolate.
spalde#
- scipy.interpolate.spalde(x, tck)[source]#
在给定一个(或一组)点上,评估B样条及其所有阶(最高为样条的度 k,其中0阶为样条本身)的导数。
旧版
此函数被视为旧版,将不再接收更新。虽然我们目前没有移除它的计划,但建议新代码使用更现代的替代方案。具体来说,我们建议构建一个
BSpline对象,并在循环或列表推导中评估其导数。- 参数:
- x类数组
用于评估导数的点或一组点。请注意,对于每个 x,必须满足
t(k) <= x <= t(n-k+1)。- tck元组
包含节点向量、B样条系数以及要计算其导数的样条的度 k 的元组 (t,c,k)。
- 返回:
- results{ndarray, ndarray 列表}
一个数组(或数组列表),包含每个点 x 的所有导数,最高到 k 阶(包括 k 阶),其中第一个元素是样条本身。
另请参阅
参考文献
[1]de Boor C : On calculating with b-splines, J. Approximation Theory 6 (1972) 50-62.
[2]Cox M.G. : The numerical evaluation of b-splines, J. Inst. Maths applics 10 (1972) 134-149.
[3]Dierckx P. : Curve and surface fitting with splines, Monographs on Numerical Analysis, Oxford University Press, 1993.
示例
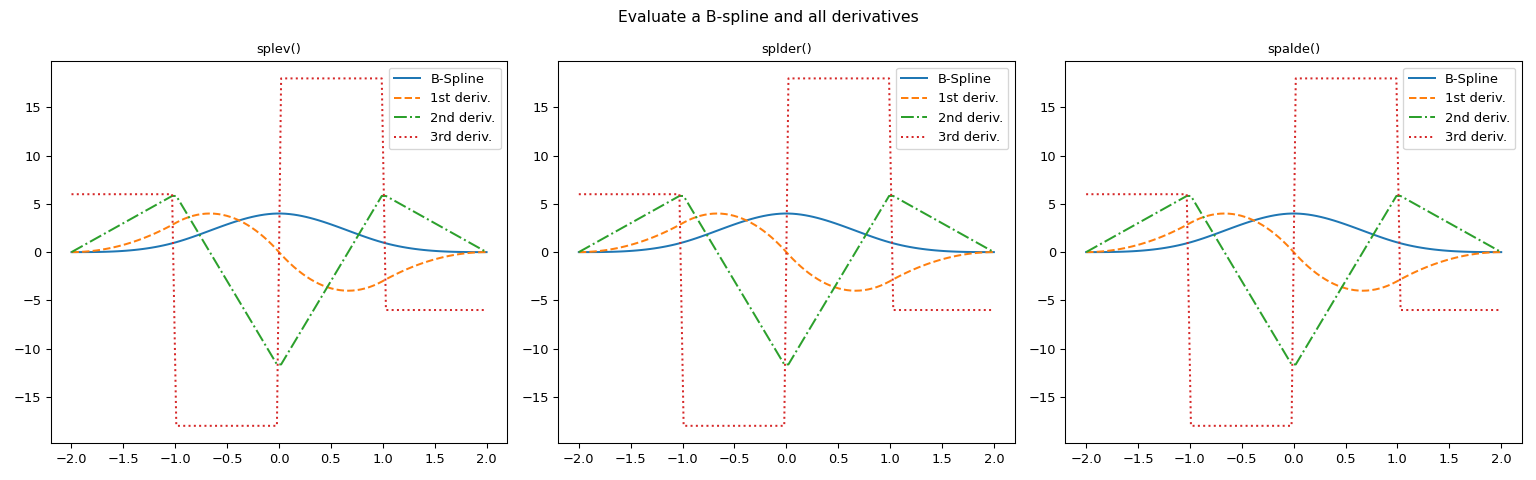
计算B样条的导数有几种方法。在此示例中,我们将演示
spalde等同于调用splev和splder。>>> import numpy as np >>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> from scipy.interpolate import BSpline, spalde, splder, splev
>>> # Store characteristic parameters of a B-spline >>> tck = ((-2, -2, -2, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2), # knots ... (0, 0, 0, 6, 0, 0, 0), # coefficients ... 3) # degree (cubic) >>> # Instance a B-spline object >>> # `BSpline` objects are preferred, except for spalde() >>> bspl = BSpline(tck[0], tck[1], tck[2]) >>> # Generate extra points to get a smooth curve >>> x = np.linspace(min(tck[0]), max(tck[0]), 100)
评估曲线和所有导数
>>> # The order of derivative must be less or equal to k, the degree of the spline >>> # Method 1: spalde() >>> f1_y_bsplin = [spalde(i, tck)[0] for i in x ] # The B-spline itself >>> f1_y_deriv1 = [spalde(i, tck)[1] for i in x ] # 1st derivative >>> f1_y_deriv2 = [spalde(i, tck)[2] for i in x ] # 2nd derivative >>> f1_y_deriv3 = [spalde(i, tck)[3] for i in x ] # 3rd derivative >>> # You can reach the same result by using `splev`and `splder` >>> f2_y_deriv3 = splev(x, bspl, der=3) >>> f3_y_deriv3 = splder(bspl, n=3)(x)
>>> # Generate a figure with three axes for graphic comparison >>> fig, (ax1, ax2, ax3) = plt.subplots(1, 3, figsize=(16, 5)) >>> suptitle = fig.suptitle(f'Evaluate a B-spline and all derivatives') >>> # Plot B-spline and all derivatives using the three methods >>> orders = range(4) >>> linetypes = ['-', '--', '-.', ':'] >>> labels = ['B-Spline', '1st deriv.', '2nd deriv.', '3rd deriv.'] >>> functions = ['splev()', 'splder()', 'spalde()'] >>> for order, linetype, label in zip(orders, linetypes, labels): ... ax1.plot(x, splev(x, bspl, der=order), linetype, label=label) ... ax2.plot(x, splder(bspl, n=order)(x), linetype, label=label) ... ax3.plot(x, [spalde(i, tck)[order] for i in x], linetype, label=label) >>> for ax, function in zip((ax1, ax2, ax3), functions): ... ax.set_title(function) ... ax.legend() >>> plt.tight_layout() >>> plt.show()