remez#
- scipy.signal.remez(numtaps, bands, desired, *, weight=None, type='bandpass', maxiter=25, grid_density=16, fs=None)[source]#
使用 Remez 交换算法计算最优极小极大滤波器。
使用 Remez 交换算法计算有限脉冲响应(FIR)滤波器的系数,该滤波器的传递函数在指定频带内使期望增益和实现增益之间的最大误差最小化。
- 参数:
- numtapsint
滤波器中所需的抽头数。抽头数是滤波器中的项数,即滤波器阶数加一。
- bandsarray_like
包含频带边缘的单调序列。所有元素必须是非负数且小于采样频率(由 fs 给出)的一半。
- desiredarray_like
一个序列,其大小为 bands 的一半,包含每个指定频带中的期望增益。
- weightarray_like, optional
给予每个频带区域的相对权重。weight 的长度必须是 bands 长度的一半。
- type{‘bandpass’, ‘differentiator’, ‘hilbert’}, optional
滤波器类型
‘bandpass’ : 频带内平坦响应。这是默认值。
‘differentiator’ : 频带内频率比例响应。
- ‘hilbert’具有奇对称性的滤波器,即 III 型
(偶数阶)或 IV 型(奇数阶)线性相位滤波器。
- maxiterint, optional
算法的最大迭代次数。默认值为 25。
- grid_densityint, optional
网格密度。
remez中使用的密集网格的大小为(numtaps + 1) * grid_density。默认值为 16。- fsfloat, optional
信号的采样频率。默认值为 1。
- 返回:
- outndarray
一个秩为 1 的数组,包含最优(在极小极大意义上)滤波器的系数。
另请参阅
参考文献
[1]J. H. McClellan and T. W. Parks, “A unified approach to the design of optimum FIR linear phase digital filters”, IEEE Trans. Circuit Theory, vol. CT-20, pp. 697-701, 1973.
[2]J. H. McClellan, T. W. Parks and L. R. Rabiner, “A Computer Program for Designing Optimum FIR Linear Phase Digital Filters”, IEEE Trans. Audio Electroacoust., vol. AU-21, pp. 506-525, 1973.
示例
在这些示例中,
remez用于设计低通、高通、带通和带阻滤波器。定义每个滤波器的参数是滤波器阶数、频带边界、边界的过渡宽度、每个频带中期望的增益以及采样频率。在所有示例中,我们将使用 22050 Hz 的采样频率。在每个示例中,每个频带中期望的增益要么是 0(对于阻带),要么是 1(对于通带)。
freqz用于计算每个滤波器的频率响应,下面定义的实用函数plot_response用于绘制响应。>>> import numpy as np >>> from scipy import signal >>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
>>> fs = 22050 # Sample rate, Hz
>>> def plot_response(w, h, title): ... "Utility function to plot response functions" ... fig = plt.figure() ... ax = fig.add_subplot(111) ... ax.plot(w, 20*np.log10(np.abs(h))) ... ax.set_ylim(-40, 5) ... ax.grid(True) ... ax.set_xlabel('Frequency (Hz)') ... ax.set_ylabel('Gain (dB)') ... ax.set_title(title)
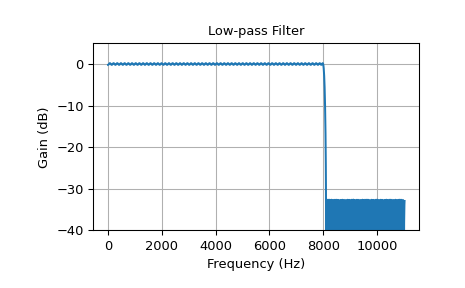
第一个示例是低通滤波器,截止频率为 8 kHz。滤波器长度为 325,从通带到阻带的过渡宽度为 100 Hz。
>>> cutoff = 8000.0 # Desired cutoff frequency, Hz >>> trans_width = 100 # Width of transition from pass to stop, Hz >>> numtaps = 325 # Size of the FIR filter. >>> taps = signal.remez(numtaps, [0, cutoff, cutoff + trans_width, 0.5*fs], ... [1, 0], fs=fs) >>> w, h = signal.freqz(taps, [1], worN=2000, fs=fs) >>> plot_response(w, h, "Low-pass Filter") >>> plt.show()
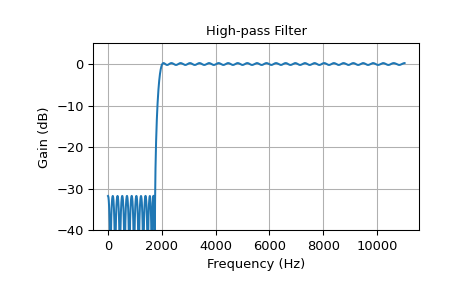
此示例展示了一个高通滤波器
>>> cutoff = 2000.0 # Desired cutoff frequency, Hz >>> trans_width = 250 # Width of transition from pass to stop, Hz >>> numtaps = 125 # Size of the FIR filter. >>> taps = signal.remez(numtaps, [0, cutoff - trans_width, cutoff, 0.5*fs], ... [0, 1], fs=fs) >>> w, h = signal.freqz(taps, [1], worN=2000, fs=fs) >>> plot_response(w, h, "High-pass Filter") >>> plt.show()
此示例展示了一个带通滤波器,通带范围从 2 kHz 到 5 kHz。过渡宽度为 260 Hz,滤波器长度为 63,比其他示例小
>>> band = [2000, 5000] # Desired pass band, Hz >>> trans_width = 260 # Width of transition from pass to stop, Hz >>> numtaps = 63 # Size of the FIR filter. >>> edges = [0, band[0] - trans_width, band[0], band[1], ... band[1] + trans_width, 0.5*fs] >>> taps = signal.remez(numtaps, edges, [0, 1, 0], fs=fs) >>> w, h = signal.freqz(taps, [1], worN=2000, fs=fs) >>> plot_response(w, h, "Band-pass Filter") >>> plt.show()
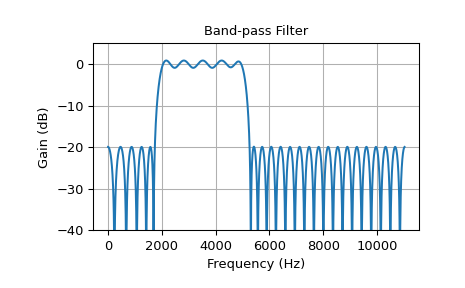
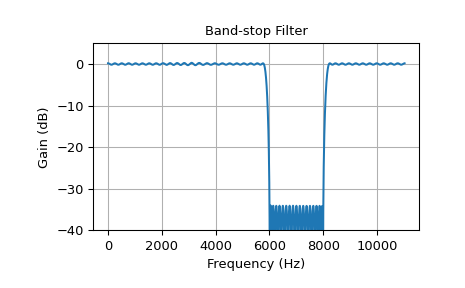
低阶导致更高的波纹和更不陡峭的过渡。
下一个示例展示了一个带阻滤波器。
>>> band = [6000, 8000] # Desired stop band, Hz >>> trans_width = 200 # Width of transition from pass to stop, Hz >>> numtaps = 175 # Size of the FIR filter. >>> edges = [0, band[0] - trans_width, band[0], band[1], ... band[1] + trans_width, 0.5*fs] >>> taps = signal.remez(numtaps, edges, [1, 0, 1], fs=fs) >>> w, h = signal.freqz(taps, [1], worN=2000, fs=fs) >>> plot_response(w, h, "Band-stop Filter") >>> plt.show()