scipy.special.
jnyn_zeros#
- scipy.special.jnyn_zeros(n, nt)[source]#
计算 Bessel 函数 Jn(x), Jn’(x), Yn(x), 和 Yn’(x) 的 nt 个零点。
返回长度为 nt 的 4 个数组,分别对应于 Jn(x), Jn’(x), Yn(x), 和 Yn’(x) 的前 nt 个零点。零点按升序返回。
- 参数:
- nint
Bessel 函数的阶数
- ntint
要计算的零点的个数 (<=1200)
- 返回:
- Jnndarray
Jn 的前 nt 个零点
- Jnpndarray
Jn’ 的前 nt 个零点
- Ynndarray
Yn 的前 nt 个零点
- Ynpndarray
Yn’ 的前 nt 个零点
参考文献
[1]Zhang, Shanjie and Jin, Jianming. “Computation of Special Functions”, John Wiley and Sons, 1996, chapter 5. https://people.sc.fsu.edu/~jburkardt/f77_src/special_functions/special_functions.html
示例
计算 \(J_1\), \(J_1'\), \(Y_1\) 和 \(Y_1'\) 的前三个根。
>>> from scipy.special import jnyn_zeros >>> jn_roots, jnp_roots, yn_roots, ynp_roots = jnyn_zeros(1, 3) >>> jn_roots, yn_roots (array([ 3.83170597, 7.01558667, 10.17346814]), array([2.19714133, 5.42968104, 8.59600587]))
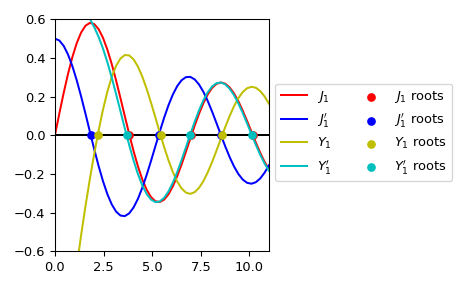
绘制 \(J_1\), \(J_1'\), \(Y_1\), \(Y_1'\) 及其根。
>>> import numpy as np >>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> from scipy.special import jnyn_zeros, jvp, jn, yvp, yn >>> jn_roots, jnp_roots, yn_roots, ynp_roots = jnyn_zeros(1, 3) >>> fig, ax = plt.subplots() >>> xmax= 11 >>> x = np.linspace(0, xmax) >>> x[0] += 1e-15 >>> ax.plot(x, jn(1, x), label=r"$J_1$", c='r') >>> ax.plot(x, jvp(1, x, 1), label=r"$J_1'$", c='b') >>> ax.plot(x, yn(1, x), label=r"$Y_1$", c='y') >>> ax.plot(x, yvp(1, x, 1), label=r"$Y_1'$", c='c') >>> zeros = np.zeros((3, )) >>> ax.scatter(jn_roots, zeros, s=30, c='r', zorder=5, ... label=r"$J_1$ roots") >>> ax.scatter(jnp_roots, zeros, s=30, c='b', zorder=5, ... label=r"$J_1'$ roots") >>> ax.scatter(yn_roots, zeros, s=30, c='y', zorder=5, ... label=r"$Y_1$ roots") >>> ax.scatter(ynp_roots, zeros, s=30, c='c', zorder=5, ... label=r"$Y_1'$ roots") >>> ax.hlines(0, 0, xmax, color='k') >>> ax.set_ylim(-0.6, 0.6) >>> ax.set_xlim(0, xmax) >>> ax.legend(ncol=2, bbox_to_anchor=(1., 0.75)) >>> plt.tight_layout() >>> plt.show()