scipy.spatial.KDTree.
query_ball_point#
- KDTree.query_ball_point(x, r, p=2.0, eps=0, workers=1, return_sorted=None, return_length=False)[source]#
查找点 x 距离 r 内的所有点。
- 参数:
- xarray_like, 形状 元组 + (self.m,)
要搜索邻居的点。
- rarray_like, float
要返回的点的半径,必须广播到 x 的长度。
- pfloat, 可选
要使用的 Minkowski p-范数。应在 [1, inf] 范围内。如果可能发生溢出,有限的大 p 可能会导致 ValueError。
- eps非负浮点数, 可选
近似搜索。如果树的分支的最近点距离大于
r / (1 + eps),则不探索这些分支;如果其最远点比r * (1 + eps)更近,则批量添加分支。- workersint, 可选
要调度的并行处理作业数。如果给定 -1,则使用所有处理器。默认值:1。
1.6.0 版本中添加。
- return_sortedbool, 可选
如果为 True,则对返回的索引进行排序;如果为 False,则不对其进行排序。如果为 None,则不对单点查询进行排序,但对多点查询进行排序,这是添加此选项之前的行为。
1.6.0 版本中添加。
- return_lengthbool, 可选
返回半径内的点数,而不是索引列表。
1.6.0 版本中添加。
- 返回值:
- results列表或列表数组
如果 x 是一个单点,则返回 x 的邻居的索引列表。如果 x 是点数组,则返回形状为元组的对象数组,其中包含邻居列表。
注释
如果您有许多想要查找邻居的点,则可以通过将它们放入 KDTree 并使用 query_ball_tree 来节省大量时间。
示例
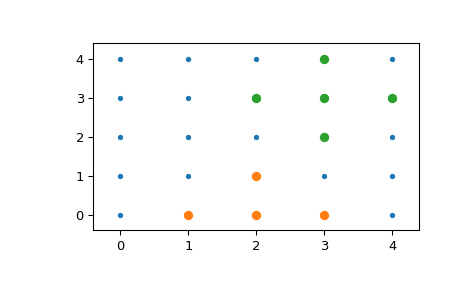
>>> import numpy as np >>> from scipy import spatial >>> x, y = np.mgrid[0:5, 0:5] >>> points = np.c_[x.ravel(), y.ravel()] >>> tree = spatial.KDTree(points) >>> sorted(tree.query_ball_point([2, 0], 1)) [5, 10, 11, 15]
查询多个点并绘制结果
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> points = np.asarray(points) >>> plt.plot(points[:,0], points[:,1], '.') >>> for results in tree.query_ball_point(([2, 0], [3, 3]), 1): ... nearby_points = points[results] ... plt.plot(nearby_points[:,0], nearby_points[:,1], 'o') >>> plt.margins(0.1, 0.1) >>> plt.show()