read#
- scipy.io.wavfile.read(filename, mmap=False)[source]#
打开一个 WAV 文件。
返回 LPCM WAV 文件的采样率(单位:样本/秒)和数据。
- 参数:
- filename字符串或打开的文件句柄
输入 WAV 文件。
- mmap布尔值,可选
是否以内存映射方式读取数据(默认值:False)。与某些位深度不兼容;请参阅“备注”。仅用于实际文件。
0.12.0 版本新增。
- 返回:
- rate整型
WAV 文件的采样率。
- datanumpy 数组
从 WAV 文件读取的数据。数据类型由文件确定;请参阅“备注”。对于单声道 WAV 文件,数据是 1-D 的;否则是 (Nsamples, Nchannels) 形状的 2-D 数据。如果传递的是没有 C 风格文件描述符的类文件输入(例如,
io.BytesIO),则此数据将不可写入。
备注
常见数据类型: [1]
WAV 格式
最小值
最大值
NumPy dtype
32 位浮点
-1.0
+1.0
float32
32 位整数 PCM
-2147483648
+2147483647
int32
24 位整数 PCM
-2147483648
+2147483392
int32
16 位整数 PCM
-32768
+32767
int16
8 位整数 PCM
0
255
uint8
WAV 文件可以指定任意位深度,此函数支持读取从 1 到 64 位的任何整数 PCM 深度。数据以左对齐格式返回,采用最小兼容的 numpy 整型。8 位及以下是无符号的,而 9 位及以上是有符号的。
例如,24 位数据将存储为 int32,其中 24 位数据的 MSB 存储在 int32 的 MSB 处,通常最低有效字节为 0x00。(然而,如果文件实际包含超出其指定位深度的数据,这些位也将被读取并输出。[2])
这种位对齐和符号与 WAV 的原生内部格式匹配,允许对每样本使用 1、2、4 或 8 字节的 WAV 文件进行内存映射(因此 24 位文件不能内存映射,但 32 位可以)。
支持 32 位或 64 位 IEEE 浮点 PCM 格式,无论是否使用 mmap。超出 [-1, +1] 的值不会被裁剪。
不支持非线性 PCM(mu-law,A-law)。
参考文献
[1]IBM 公司和微软公司,《多媒体编程接口和数据规范 1.0》,“样本数据格式”部分,1991 年 8 月 http://www.tactilemedia.com/info/MCI_Control_Info.html
[2]Adobe Systems Incorporated,《Adobe Audition 3 用户指南》,“音频文件格式:24 位打包整数(类型 1,20 位)”部分,2007 年
示例
>>> from os.path import dirname, join as pjoin >>> from scipy.io import wavfile >>> import scipy.io
从 tests/data 目录获取示例 .wav 文件的文件名。
>>> data_dir = pjoin(dirname(scipy.io.__file__), 'tests', 'data') >>> wav_fname = pjoin(data_dir, 'test-44100Hz-2ch-32bit-float-be.wav')
加载 .wav 文件内容。
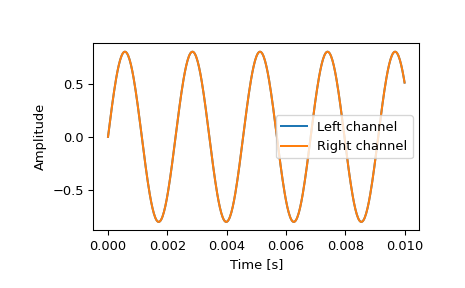
>>> samplerate, data = wavfile.read(wav_fname) >>> print(f"number of channels = {data.shape[1]}") number of channels = 2 >>> length = data.shape[0] / samplerate >>> print(f"length = {length}s") length = 0.01s
绘制波形。
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> import numpy as np >>> time = np.linspace(0., length, data.shape[0]) >>> plt.plot(time, data[:, 0], label="Left channel") >>> plt.plot(time, data[:, 1], label="Right channel") >>> plt.legend() >>> plt.xlabel("Time [s]") >>> plt.ylabel("Amplitude") >>> plt.show()