scipy.spatial.
SphericalVoronoi#
- class scipy.spatial.SphericalVoronoi(points, radius=1, center=None, threshold=1e-06)[source]#
球面上的 Voronoi 图。
0.18.0 版新增。
- 参数:
- points浮点型 ndarray,形状为 (npoints, ndim)
用于构建球面 Voronoi 图的点的坐标。
- radius浮点型,可选
球体的半径(默认值:1)
- center浮点型 ndarray,形状为 (ndim,)
球体中心(默认值:原点)
- threshold浮点型
用于检测重复点以及点与球体参数之间不匹配的阈值。(默认值:1e-06)
- 属性:
- points双精度数组,形状为 (npoints, ndim)
用于生成 Voronoi 图的 ndim 维点
- radius双精度
球体半径
- center双精度数组,形状为 (ndim,)
球体中心
- vertices双精度数组,形状为 (nvertices, ndim)
对应于点的 Voronoi 顶点
- regions整数列表的列表,形状为 (npoints, _ )
第 n 个条目是一个列表,包含属于 points 中第 n 个点的顶点的索引
方法
计算 Voronoi 区域的面积。
- 抛出:
- ValueError
如果 points 中存在重复项。如果提供的 radius 与 points 不一致。
另请参阅
VoronoiN 维常规 Voronoi 图。
备注
球面 Voronoi 图算法的步骤如下:计算输入点(生成器)的凸包,这等同于它们在球体表面上的 Delaunay 三角剖分 [Caroli]。然后使用凸包邻域信息来围绕每个生成器对 Voronoi 区域顶点进行排序。后一种方法比基于角度的 Voronoi 区域顶点排序方法对浮点问题的影响要小得多。
对球面 Voronoi 算法性能的实证评估表明其时间复杂度为二次方(对数线性是最佳的,但算法实现更具挑战性)。
参考文献
[Caroli]Caroli 等人。球体上或接近球体点的稳健高效 Delaunay 三角剖分。研究报告 RR-7004, 2009。
[VanOosterom]Van Oosterom 和 Strackee。《平面三角形的立体角》。IEEE 生物医学工程汇刊,2,1983,第 125–126 页。
示例
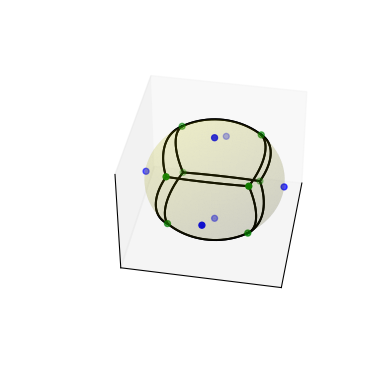
导入一些模块并在立方体上取一些点
>>> import numpy as np >>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> from scipy.spatial import SphericalVoronoi, geometric_slerp >>> from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import proj3d >>> # set input data >>> points = np.array([[0, 0, 1], [0, 0, -1], [1, 0, 0], ... [0, 1, 0], [0, -1, 0], [-1, 0, 0], ])
计算球面 Voronoi 图
>>> radius = 1 >>> center = np.array([0, 0, 0]) >>> sv = SphericalVoronoi(points, radius, center)
生成图表
>>> # sort vertices (optional, helpful for plotting) >>> sv.sort_vertices_of_regions() >>> t_vals = np.linspace(0, 1, 2000) >>> fig = plt.figure() >>> ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d') >>> # plot the unit sphere for reference (optional) >>> u = np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, 100) >>> v = np.linspace(0, np.pi, 100) >>> x = np.outer(np.cos(u), np.sin(v)) >>> y = np.outer(np.sin(u), np.sin(v)) >>> z = np.outer(np.ones(np.size(u)), np.cos(v)) >>> ax.plot_surface(x, y, z, color='y', alpha=0.1) >>> # plot generator points >>> ax.scatter(points[:, 0], points[:, 1], points[:, 2], c='b') >>> # plot Voronoi vertices >>> ax.scatter(sv.vertices[:, 0], sv.vertices[:, 1], sv.vertices[:, 2], ... c='g') >>> # indicate Voronoi regions (as Euclidean polygons) >>> for region in sv.regions: ... n = len(region) ... for i in range(n): ... start = sv.vertices[region][i] ... end = sv.vertices[region][(i + 1) % n] ... result = geometric_slerp(start, end, t_vals) ... ax.plot(result[..., 0], ... result[..., 1], ... result[..., 2], ... c='k') >>> ax.azim = 10 >>> ax.elev = 40 >>> _ = ax.set_xticks([]) >>> _ = ax.set_yticks([]) >>> _ = ax.set_zticks([]) >>> fig.set_size_inches(4, 4) >>> plt.show()