scipy.signal.
max_len_seq#
- scipy.signal.max_len_seq(nbits, state=None, length=None, taps=None)[source]#
最大长度序列 (MLS) 生成器。
- 参数:
- nbitsint
要使用的比特数。生成序列的长度将为
(2**nbits) - 1。请注意,生成长序列(例如,大于nbits == 16)可能需要很长时间。- statearray_like, optional
如果为数组,则长度必须为
nbits,并将转换为二进制 (bool) 表示。如果为 None,将使用全一的种子,生成可重复的表示。如果state全为零,则会引发错误,因为这是无效的。默认值:None。- lengthint, optional
要计算的样本数。如果为 None,则计算整个长度
(2**nbits) - 1。- tapsarray_like, optional
要使用的多项式抽头(例如,8 位序列的
[7, 6, 1])。如果为 None,将自动选择抽头(最多nbits == 32)。
- 返回:
- seqarray
生成的由 0 和 1 组成的 MLS 序列。
- statearray
移位寄存器的最终状态。
备注
MLS 生成算法在以下链接中通用描述:
抽头的默认值特别取自以下链接中每个
nbits值的第一个选项:自 0.15.0 版本加入。
示例
MLS 使用二进制约定
>>> from scipy.signal import max_len_seq >>> max_len_seq(4)[0] array([1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0], dtype=int8)
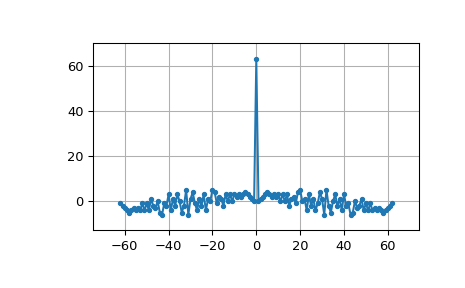
MLS 具有白频谱(直流除外)
>>> import numpy as np >>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> from numpy.fft import fft, ifft, fftshift, fftfreq >>> seq = max_len_seq(6)[0]*2-1 # +1 and -1 >>> spec = fft(seq) >>> N = len(seq) >>> plt.plot(fftshift(fftfreq(N)), fftshift(np.abs(spec)), '.-') >>> plt.margins(0.1, 0.1) >>> plt.grid(True) >>> plt.show()
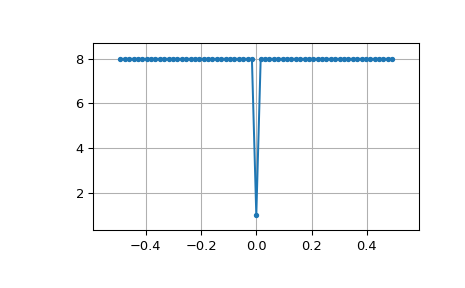
MLS 的循环自相关是脉冲
>>> acorrcirc = ifft(spec * np.conj(spec)).real >>> plt.figure() >>> plt.plot(np.arange(-N/2+1, N/2+1), fftshift(acorrcirc), '.-') >>> plt.margins(0.1, 0.1) >>> plt.grid(True) >>> plt.show()
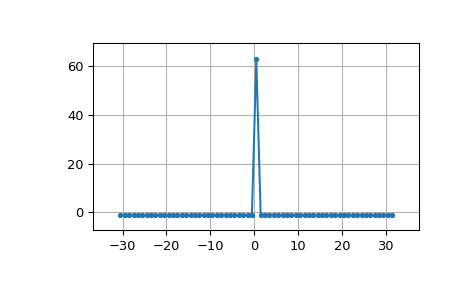
MLS 的线性自相关近似为脉冲
>>> acorr = np.correlate(seq, seq, 'full') >>> plt.figure() >>> plt.plot(np.arange(-N+1, N), acorr, '.-') >>> plt.margins(0.1, 0.1) >>> plt.grid(True) >>> plt.show()